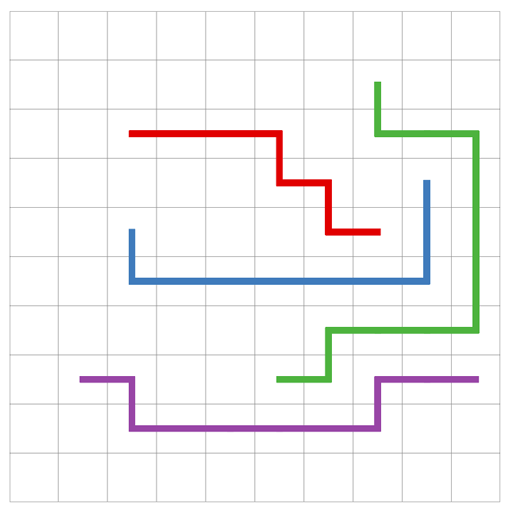
This example shows how to use the Pathfinding.ITraversalProvider interface to generate paths like on a circuit-board.I.e paths that do not share any node. The image below shows a test case when using the script to calculate 4 paths on a small grid. The visualization of the paths has been improved manually using an external photo-editing application.
The code has intentionally been left simple, so very little error checking and special case handling is done.
Note that finding paths on a circuit-board in an optimal way is a very hard problem (NP-Complete). For further information about that, see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multi-commodity_flow_problem.
Attach this script to any GameObject and fill in the 'items' array with the start end endpoints of each path.
- See also
- Utilities for turn-based games
-
Pathfinding.ITraversalProvider
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class CircuitBoardExample : MonoBehaviour {
public class Item {
public Transform start;
public Transform end;
}
public Item[] items;
class Blocker : ITraversalProvider {
public HashSet<GraphNode> blockedNodes = new HashSet<GraphNode>();
public bool CanTraverse (Path path, GraphNode node) {
return DefaultITraversalProvider.CanTraverse(path, node) && !blockedNodes.Contains(node);
}
public uint GetTraversalCost (Path path, GraphNode node) {
return DefaultITraversalProvider.GetTraversalCost(path, node);
}
}
void Update () {
var traversalProvider = new Blocker();
for (int index = 0; index < items.Length; index++) {
var item = items[index];
ABPath path = ABPath.Construct(item.start.position, item.end.position);
path.traversalProvider = traversalProvider;
path.BlockUntilCalculated();
foreach (var node in path.path) {
traversalProvider.blockedNodes.Add(node);
}
Color color = AstarMath.IntToColor(index, 0.5f);
for (int i = 0; i < path.vectorPath.Count - 1; i++) {
Debug.DrawLine(path.vectorPath[i], path.vectorPath[i+1], color);
}
}
}
}